JFrog Artifactory - Package Repository
Many enterprises leverage JFrog Artifactory to;
-
Proxy all package downloads. This allows administrators to ensure packages are only being downloaded from specified source like Maven Central, and not arbitrary websites. Think of this use case like the Apple app store and how you can only download apps from there, unless the device is jailbroken.
-
Host custom packages. Most large enterprises will write their own components that may be used across several enterprise applications, and Artifactory provides services to host them.
It’s critical to know if your customer is leveraging Artifactory for these use cases because if it is not integrated with Snyk there will be large occurrences of false negatives. The symptoms will be;
-
Custom packages that show 0 issues. This may be fine, however there will likely be many that include transitive open source dependencies that Snyk will not be able to see without Artifactory integration.
-
Unknown package information. This happens when Snyk can’t access a parent pom, likely because it’s hosted on a private Artifactory.
Step 1 - Create an Artifactory Container
If you’d like to see this work for yourself you’ll need an Artifactory server, JFrog Artifactory Container.
Step 2 - Feature Flags
Navigate to admin panel and enable artifactory and artifactoryBroker on the Organization.
Step 3 - Get a Broker Token
-
Navigate to the Snyk
Organization, Settings, andArtifactory. -
Toggle
Broker to On. This will generate the token. I had an issue where after running the Broker with this token, then testing the Broker from https://app.snyk.io/admin the tests failed. Deleting the token from admin panel and generating a new one there made the test successful.
Step 4 - Start Broker
There are a few environment variables that needed modification:
-
For
ARTIFACTORY_URL-
Make sure the http is present. Broker defaults to https on internal connections, but Artifactory does not deploy this way by default.
-
Specify the username and password after http://. Unfortunately URL encoding the credentials is the only supported authentication method currently.
-
Make the IP address of Artifactory the internal IP address of your system. If you make this localhost, the Broker container will be trying to talk to iteself, so by making it your system IP address the traffic will leave the container and get to Artifactory.
-
The port is 8082 (not 8081).
-
The path is /artifactory.
-
-
Ensure
INSECURE_DOWNSTREAM=“true” to avoid problems with Broker expecting an SSL certificate from Artifactory that’s not there.
docker run --restart=always \ -p 8000:8000 \ -e BROKER_TOKEN=[Sensitive data redacted] \ -e ARTIFACTORY_URL=http://admin:[email protected]:8082/artifactory \ -e INSECURE_DOWNSTREAM="true" \ snyk/broker:artifactory
Check that Broker is ok.
-
You should see a message in the Broker container log (either on the terminal you started it on, or run
docker logs <container ID>) indicating that the websocket connection is established. -
Check the status of Broker by logging into https://app.snyk.io/admin. Navigate to the Organization, and find the Broker tokens. From there you can test the connection and you’re looking for a 200 response. A few people have noticed that the local port of 8000 is not listening as expected. Even logging directly into the container revealed it is not running so you will not be able to navigate to http://localhost/healthcheck or http://localhost/systemcheck.
Step 5 - Demonstrate What Bad Looks Like
-
Completing all of the steps in
Step 1of this guide is essential! -
Import the
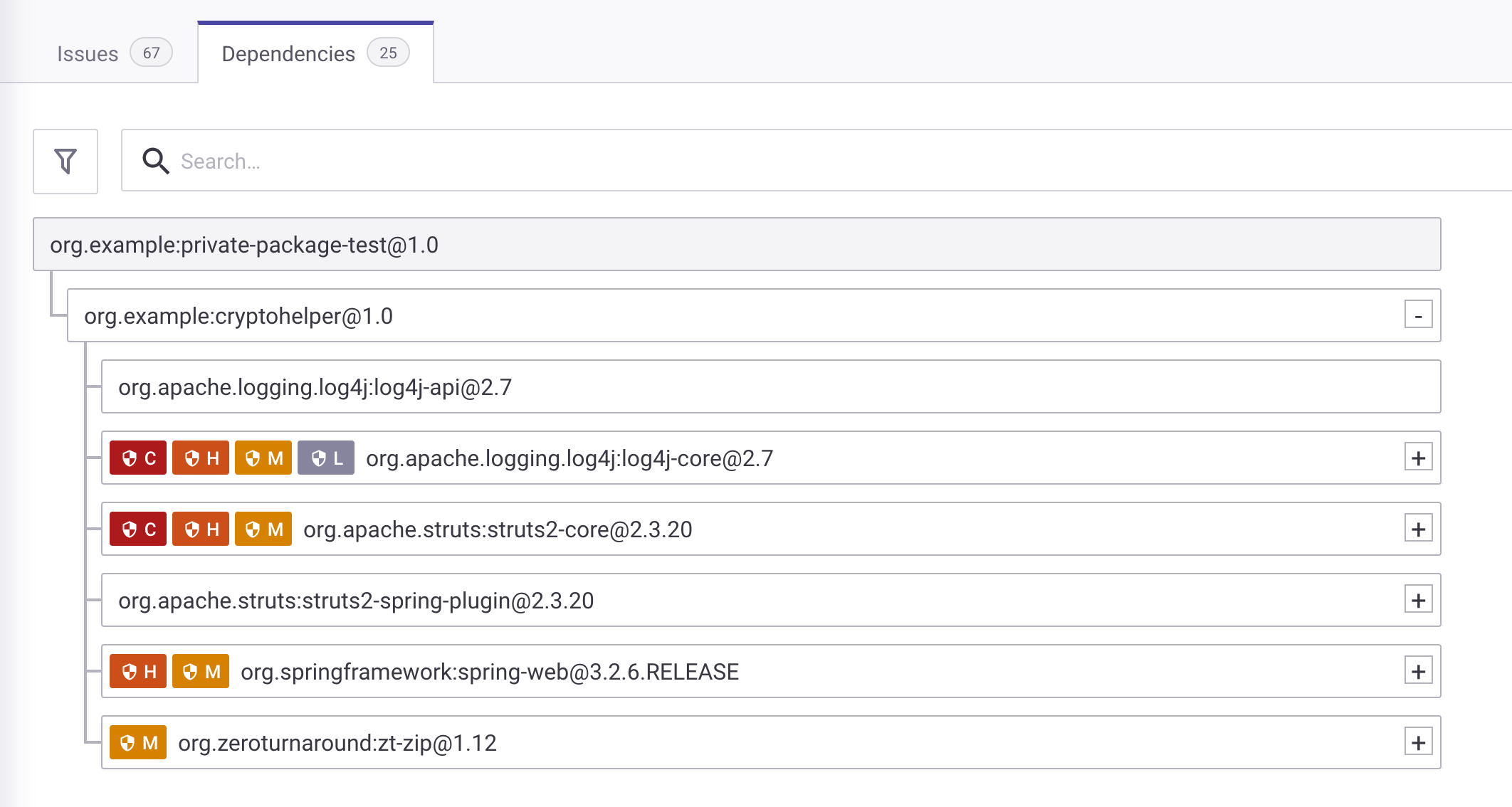
java-goof-artifactoryrepository from your SCM into the Snyk Organization with Artifactory enabled. You should see a Target with the pom.xml with 0 Issues. If you navigate to pom.xml and Dependencies you can see the custom package being referenced at least.
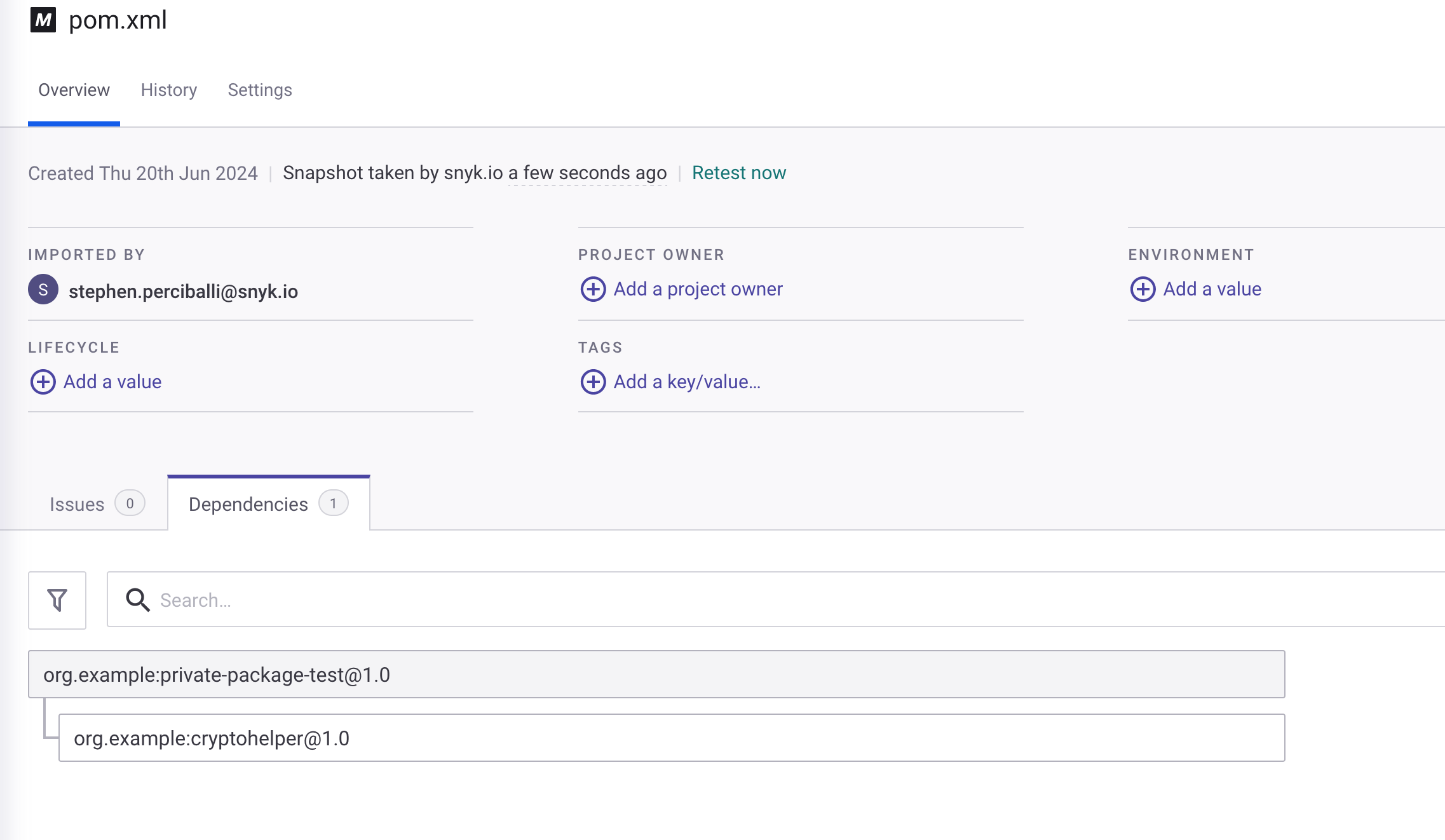
The problem here is that while this custom package may not have any known vulnerabilities (because it’s a private package), it does include transitive dependencies. Snyk doesn’t currently have access to the pom.xml which is hosted in Artifactory for cryptohelper, creating a major blind spot.
Step 6 - Update the Language Settings
In order for Snyk to understand where the pom.xml is for this custom/private application we need to modify Language Settings.
-
Navigate to the Snyk
Organization, Settings, Languages, andJava. -
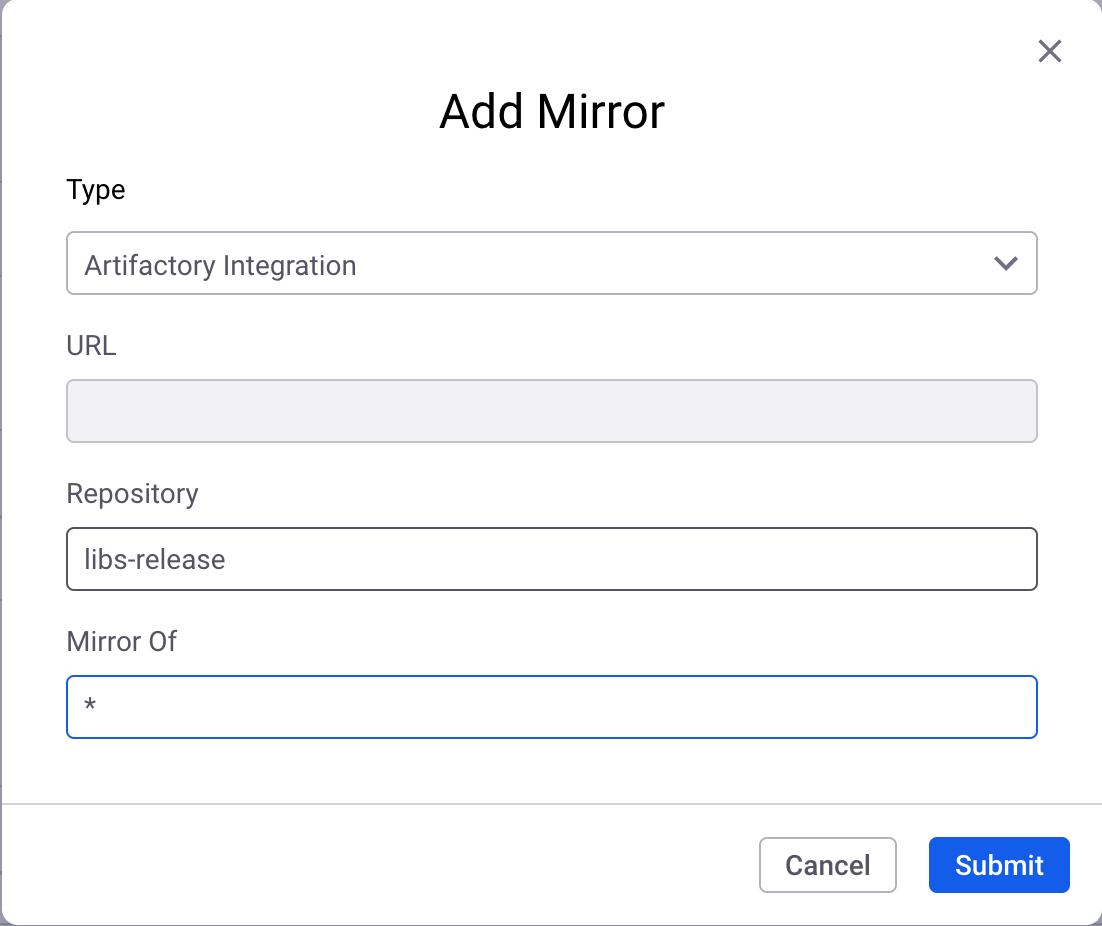
Click
Edit, andAdd Mirrors. -
For
TypechooseArtifactory Integration. -
For
Repositorytypelibs-release. -
Mirrorof type*.
Step 7 - Re-Import the Project
Re-import the repository java-goof-artifactory from your SCM. Now you should see all of the issues that you introduced by adding vulnerable, transitive, dependencies to your custom application.
Looking at the tree view of the Dependencies tab below we can see how many actual issues are brought into this environment by using the custom/private application cryptohelper.